WIP openSUSE:Factory development model
Development Model
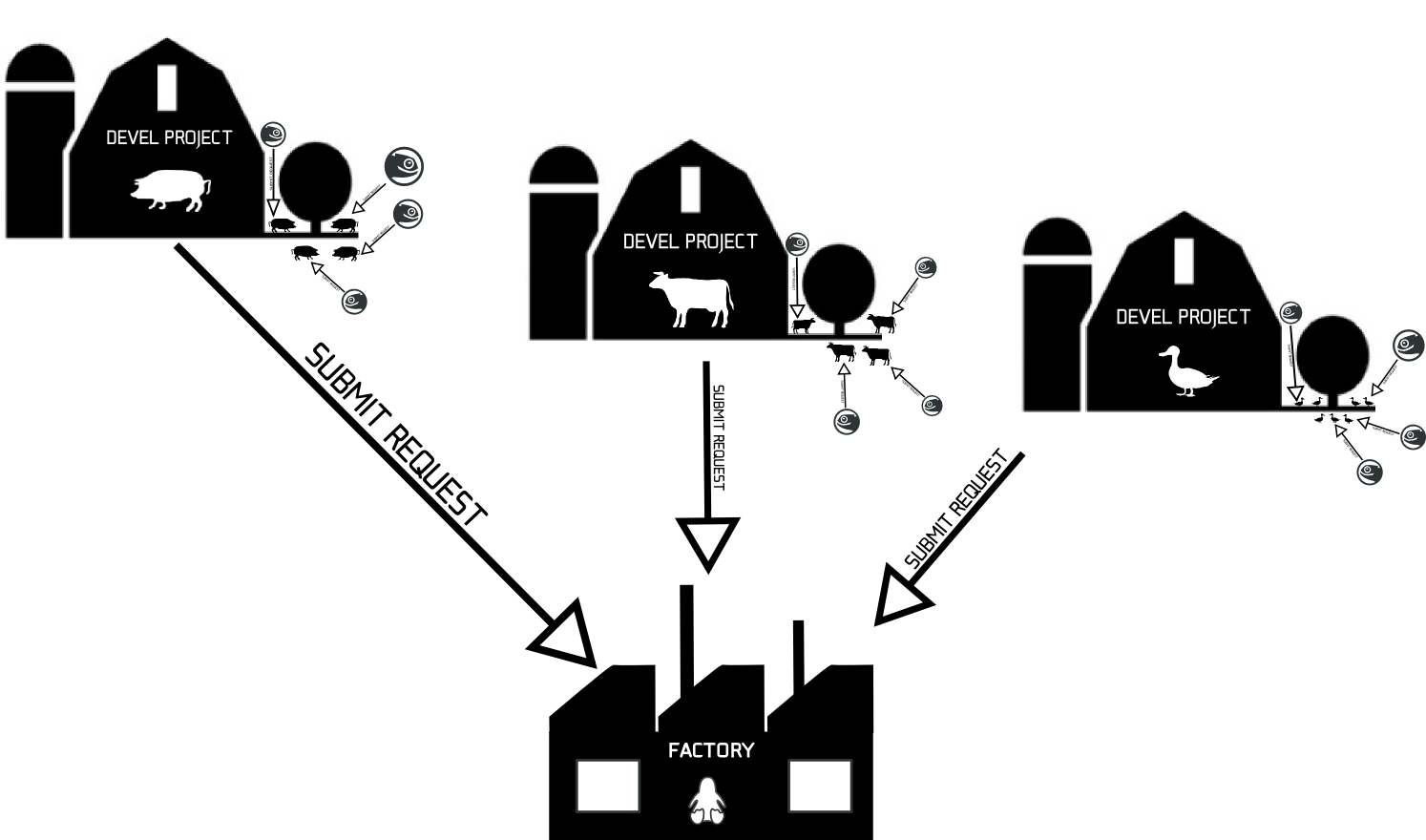
Factory is built in its own project openSUSE:Factory on the Open Build Service reference server. As you can see, it is a huge repository of packages. Development, however, does not happen directly in openSUSE:Factory but in so called devel projects. A devel project, as the name suggests, is a project where development happens for a specific group of packages. Like multimedia, GNOME, KDE or Kernel. The relation of packages in the openSUSE:Factory project to packages in the devel projects is expressed in the meta data of the packages inside openSUSE:Factory.
Devel Projects
Each devel project has its own set of processes, rules and communication channels that fits them best. The reference point for this information is the project description of their Build Service project. Devel projects are also subject to change because the world of FOSS software is constantly evolving. Certain software becomes obsolete, standards and defaults change. That means devel projects can change names, get dropped, be newly created, or change content and direction, as can packages in devel projects. The current devel projects feeding into factory can be found in the drop-down menu on top of this page. You can find a summary description of the Factory submission process here.
You can check a more detailed information about this topic.
Staging Projects
Once in a while, a specific core package (like a new version of GCC) is deemed to have the potential to break so much that the Factory Maintainers decide to create a special staging project in which Factory is build against the new package. Its developers can then fix the resulting breakage before integration back into Factory.
Staging projects can be seen as a fork of Factory in which some developer can prepare changes/updates to different packages, build them together, test them and submit them together for inclusion into Factory when everything has been tested.
Factory has been divided into three rings (0-bootstrap, 1-minimalX, 2-testDVD). The inner ring ( 0-bootstrap ) contains packages that form the most basic, minimalist system. The next ring contains ring 0 plus everything needed to run a minimal X system. Finally, the outer ring contains everything else.
When a submit request is done to a package that belongs to the inner ring the request is automatically put in a backlog for the Staging Master to review and assign it to a specific staging project. There are 9 staging projects currently, named A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J. Staging J is a special case, it's against to test non-belong-to-rings packages. Whose purpose and contained packages change over time. Each Staging Project have generated the image time to time, and test the image on openQA in order to recognize those packages would not breaks current Factory.
osc-plugin-factory is the tool what handling everything with Staging Project, the staging plugin document explains the usage of this tool.
It might be possible that other packages fail due to this submit request, in that case, those packages are added to the same staging project, so they're build against each other.
Once every package in a staging project builds successfully and test fine on openQA, the Factory Maintainer can submit it to Factory and leave it free to test other changes in the future.
Development Process Overview
The complete Development Process is detailed on this page. It consists of the following steps:
- Roadmap and Feature Planning is managed by the Release Manager who creates the initial roadmap. Meanwhile, the developers set technical goals for the distribution based on the projected release and freeze dates.
- Package Development starts in a OBS home project [8]. The Package Developer can work here without affecting anything else. Once the package is good enough a submit request to a devel project can be created.
- Devel Project Integration follows, overseen by Project Maintainers who keep an eye on the technical quality of submit requests and the overall state of a Devel Project. After successful integration, the Project Maintainers create Submit Requests for Factory.
- The Review Process makes sure that all packages on their way to Factory go through 4 (sometimes 5) reviews:
- Factory-Auto: an script that checks basic rules [10]
- Legal-Auto: a script checking if the license of the package is in the permitted license database [10]
- Repo-Checker: a more in depth (and slow) automatic check [10]
- Review Team: human check of the request.
- Optional: Manual Security Team check (if Legal-Auto deems that necessary)
- Factory Integration is overseen by the Factory Maintainer and the Release Managers who accept the submit requests that come from the different devel projects to Factory [9]. They mostly decide based on timing and policy factors like freezes that might be in effect as the review process has already taken care of quality. In some cases, they decide a Staging Project is needed. When a Staging Project is needed, the submit request need walk through openQA and must be have green result. Once everything goes fine, Factory Maintainer would accept that Staging Project, afterwards the submit requests what belongs to that Staging Project will checked in into Factory.
- The Quality Assurance Process (openQA) runs all the time. Periodically, ISO image are generated by OBS and ran through a predefined set of tests. If problems are found a report is created pointing to the failures in the ISO image. Currently, openQA was majorly testing Staging Project image and Factory-ToTest image.
- Factory-ToTest. In the current Factory model, Factory-ToTest represent the project that store several Factory Snapshots that are candidates to/could be released if the quality is good enough on openQA.
- Release Process. Based on timing and the results of the QA process, a milestone or beta can be released by the Release Manager. He/she takes care of the release tasks: calculate the ISO MD5/SHA1 hashes, set up the repositories, prepare and seed to the mirrors, deploy the products and kick marketing to communicate the release.
- Public Testing takes place after the milestone release, usually on real hardware and to a lesser degree in virtual machines.
Not too long after the release of the Beta (the final milestone before total freeze), the Release Team forks off the release from Factory and uses the Maintenance update process to stabilize the release.
- You can check a more detailed information about openSUSE Development process.
- Find out more about the release process here.
- Find out what is what in the Glossary.
Governance Model
Bug fixes and new features have to be first committed to a devel project, and from there will be forwarded to the main openSUSE Factory project. Because of this, the governance of the Factory project is also further broken down.
Responsibilities
| Package | Devel Project | Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Maintainer & Bugowner | Project Maintainer & Bugowner | Release team |
See a more detailed list of roles and responsibilities here.
Escalations
Most decisions are taken by the maintainer of the package. If the maintainer cannot take a decision, or if a conflict arises between maintainers, the devel project maintainers decide together. If the devel project maintainers also do not come to a conclusion, or a conflict between two devel projects arises, the openSUSE release team takes the decision. If the decision cannot be taken by the release team, they appeal to the openSUSE Board which tries to facilitate the decision with all the involved people. If that also is not successful, the board puts up the issue to a vote among the members.
Maintainer ==> Devel project maintainers ==> openSUSE:Release team ==> openSUSE:Board ==> openSUSE:Members Vote
You can read a more detailed information about the openSUSE/factory Development process.